Dns Caching Windows

Introduction to DNS Caching in Windows

DNS caching, also known as DNS resolution caching, is a mechanism that stores the results of DNS lookups on a local system, allowing for faster access to websites and online services. In Windows, DNS caching plays a crucial role in improving network performance and reducing the time it takes to access frequently visited websites. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNS caching in Windows, exploring its benefits, how it works, and how to manage it.
How DNS Caching Works in Windows

When you enter a URL in your web browser, your system sends a request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name into an IP address. This process is called a DNS lookup. By default, Windows stores the results of these DNS lookups in a local cache, known as the DNS resolver cache. This cache contains a list of recently accessed domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. When you visit a website again, Windows checks the cache first to see if it has a valid entry for the domain name. If it does, it uses the cached IP address instead of sending a new request to the DNS server.
Benefits of DNS Caching in Windows

The benefits of DNS caching in Windows are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Faster Browsing: By reducing the number of DNS lookups, DNS caching can significantly improve browsing speeds. * Reduced Network Traffic: Fewer DNS requests mean less network traffic, which can lead to cost savings and improved overall network performance. * Improved Reliability: DNS caching can help reduce the impact of DNS server outages or network congestion, ensuring that you can still access frequently visited websites.
Managing DNS Cache in Windows

While DNS caching is enabled by default in Windows, there may be times when you need to manage the cache manually. Here are some ways to do so: * Clearing the DNS Cache: You can clear the DNS cache using the command
ipconfig /flushdns in the Command Prompt.
* Disabling DNS Cache: You can disable DNS caching by setting the dnscache service to disabled in the Services console.
* Configuring DNS Cache Settings: You can configure DNS cache settings, such as the cache size and timeout, using the Windows Registry Editor.
💡 Note: Be cautious when modifying DNS cache settings, as it can impact network performance and stability.
Common Issues with DNS Caching in Windows

While DNS caching is generally a reliable mechanism, there are some common issues that can arise: * Cache Poisoning: Malicious attackers can attempt to poison the DNS cache with fake entries, redirecting you to phishing sites or malware. * Cache Corruption: The DNS cache can become corrupted, leading to errors and connectivity issues. * Outdated Cache Entries: The DNS cache can contain outdated entries, causing issues with websites that have recently changed their IP addresses.
Troubleshooting DNS Caching Issues in Windows
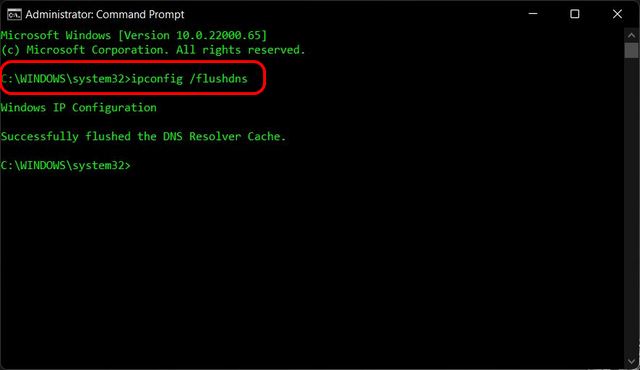
If you encounter issues with DNS caching, here are some troubleshooting steps to follow: * Clear the DNS Cache: Try clearing the DNS cache using the
ipconfig /flushdns command.
* Restart the DNS Client Service: Restart the DNS client service to see if it resolves the issue.
* Check for malware: Run a virus scan to ensure that your system is free from malware.
Best Practices for DNS Caching in Windows
To get the most out of DNS caching in Windows, follow these best practices: * Regularly clear the DNS cache: Clear the DNS cache periodically to ensure that it remains up-to-date and free from corruption. * Monitor DNS cache performance: Keep an eye on DNS cache performance to identify potential issues before they become major problems. * Implement DNS security measures: Implement DNS security measures, such as DNSSEC, to protect against cache poisoning and other DNS-based attacks.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ipconfig /flushdns | Clears the DNS cache |
| ipconfig /registerdns | Registers the system's DNS entries |
| ipconfig /displaydns | Displays the contents of the DNS cache |

In summary, DNS caching is a powerful mechanism in Windows that can significantly improve network performance and reduce the time it takes to access frequently visited websites. By understanding how DNS caching works, managing it effectively, and troubleshooting common issues, you can get the most out of this technology and enjoy a faster, more reliable browsing experience.
To recap, the key points to take away from this article are the benefits of DNS caching, how to manage the DNS cache, common issues that can arise, and best practices for optimizing DNS caching performance. By following these guidelines and staying informed about the latest developments in DNS caching, you can ensure that your Windows system is running at its best.
What is DNS caching in Windows?

+
DNS caching in Windows is a mechanism that stores the results of DNS lookups on a local system, allowing for faster access to websites and online services.
How do I clear the DNS cache in Windows?

+
You can clear the DNS cache using the command ipconfig /flushdns in the Command Prompt.
What are the benefits of DNS caching in Windows?

+
The benefits of DNS caching in Windows include faster browsing, reduced network traffic, and improved reliability.



