Spf Dkim And Dmarc

Introduction to Email Authentication Protocols

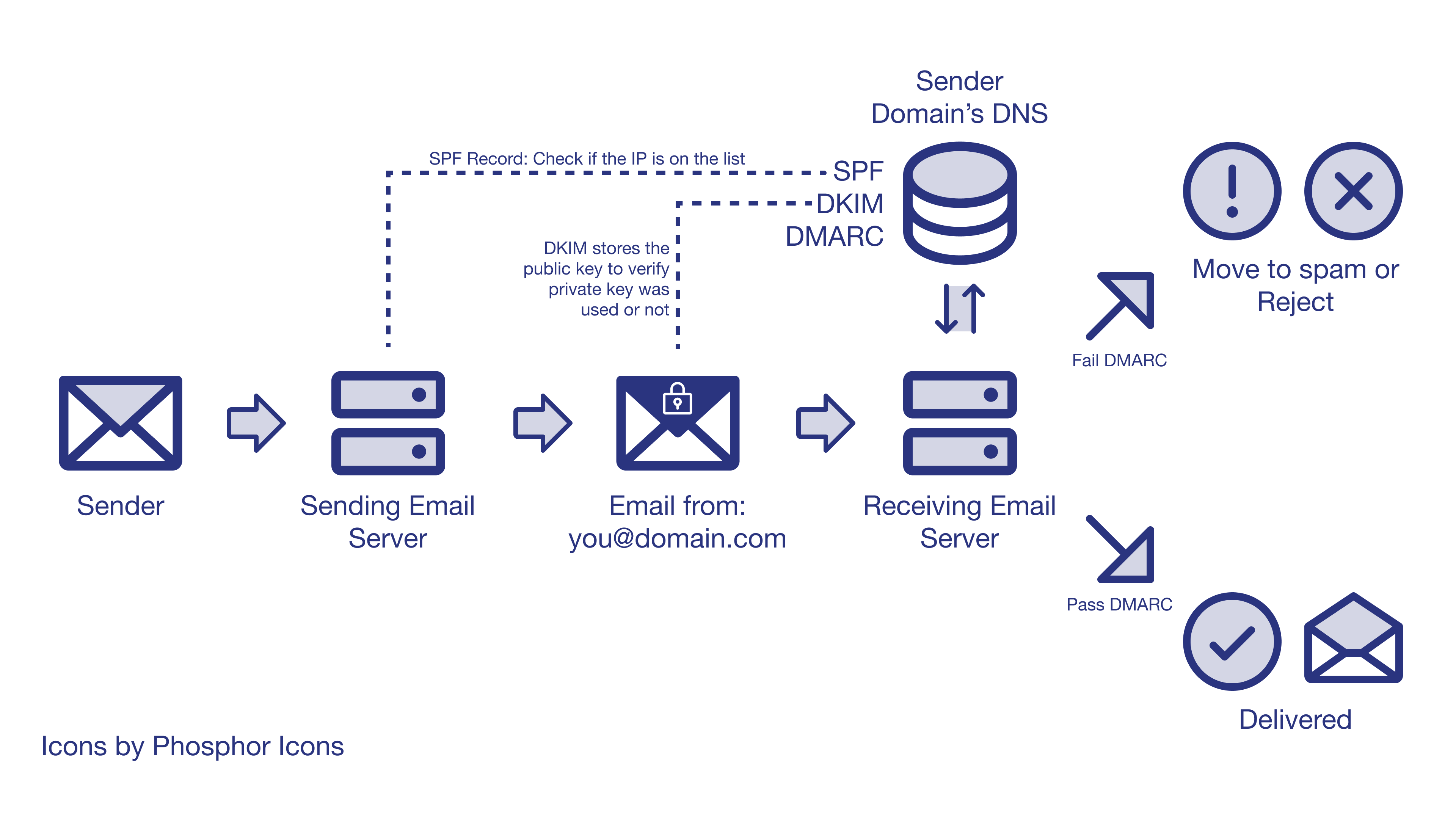
Email authentication protocols are a set of standards designed to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks. These protocols help verify the authenticity of emails, ensuring that they come from legitimate sources. There are three main email authentication protocols: SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). In this blog post, we will delve into each of these protocols, exploring their functions, benefits, and implementation processes.
Understanding SPF (Sender Policy Framework)

SPF is a protocol that allows domain owners to specify which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on their behalf. This is done by creating a TXT record in the domain’s DNS settings, which lists the IP addresses that are allowed to send emails. When an email is sent, the recipient’s email server checks the SPF record to ensure that the email is coming from an authorized IP address. If the IP address is not listed in the SPF record, the email may be flagged as spam or rejected.
📝 Note: It's essential to keep SPF records up-to-date, as changes in IP addresses or email services can affect email deliverability.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Explained

DKIM is a protocol that uses digital signatures to verify the authenticity of emails. It works by adding a digital signature to the email header, which is then verified by the recipient’s email server. This ensures that the email has not been tampered with during transmission. DKIM uses a pair of keys: a private key to sign the email and a public key to verify the signature. This provides an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for spammers to spoof emails.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)

DMARC is a protocol that builds upon SPF and DKIM. It provides a way for domain owners to specify what actions should be taken when an email fails authentication. This can include rejecting the email, quarantining it, or allowing it to pass through. DMARC also provides reporting features, which allow domain owners to monitor email authentication results and identify potential issues. This helps to improve email deliverability and prevent spam and phishing attacks.
Benefits of Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Implementing these email authentication protocols can have several benefits, including: * Improved email deliverability: By verifying the authenticity of emails, domain owners can improve their reputation and increase the chances of their emails being delivered to the recipient’s inbox. * Reduced spam and phishing attacks: By making it more difficult for spammers to spoof emails, these protocols can help reduce the number of spam and phishing attacks. * Enhanced security: These protocols provide an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept and tamper with emails.
Implementation Process

Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC requires a few steps: * Set up SPF: Create a TXT record in the domain’s DNS settings, listing the authorized IP addresses. * Set up DKIM: Generate a pair of keys and add the public key to the domain’s DNS settings. Configure the email server to sign emails with the private key. * Set up DMARC: Create a TXT record in the domain’s DNS settings, specifying the DMARC policy and reporting options. * Monitor and adjust: Monitor email authentication results and adjust the protocols as needed to ensure optimal performance.
| Protocol | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| SPF | Specifies authorized IP addresses | Improves email deliverability, reduces spam |
| DKIM | Uses digital signatures to verify authenticity | Provides additional security, prevents tampering |
| DMARC | Specifies actions for failed authentication, provides reporting | Improves email deliverability, reduces spam and phishing attacks |

In summary, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are essential email authentication protocols that help prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks. By implementing these protocols, domain owners can improve email deliverability, reduce spam and phishing attacks, and enhance security. It’s essential to understand each protocol’s functions, benefits, and implementation processes to ensure optimal performance.
What is the primary function of SPF?

+
The primary function of SPF is to specify which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain.
How does DKIM work?

+
DKIM uses digital signatures to verify the authenticity of emails. It adds a digital signature to the email header, which is then verified by the recipient’s email server.
What are the benefits of implementing DMARC?

+
The benefits of implementing DMARC include improved email deliverability, reduced spam and phishing attacks, and enhanced security.



